Types of mutations and suspected mechanism
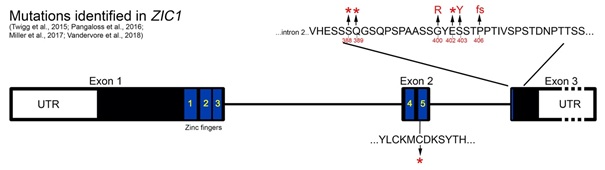
- Seven different heterozygous mutations in 8 families have been described so far comprising 4 nonsense mutations, 1 frameshift and 2 missense (Figure 1).
- Six of the mutations are clustered within 19 bp in the final exon (exon 3) of ZIC1.
- There is evidence from analysis of RNA that the nonsense and frameshift variants within exon 3 can escape nonsense mediated decay (NMD) presumably generating mutant ZIC1 proteins (with all 5 zinc-fingers intact).
- Functional analysis in Xenopus of the nonsense and missense variants in exon 3 supports a gain-of-function mechanism.
- The nonsense mutations are de novo (or presumed de novo in one case), with one occurring post-zygotically in an individual with milder features including no brain abnormalities.
- One frameshift mutation, which leads to the addition of 41 novel amino acids to the C-terminus has been reported.
- The nonsense mutation (presumed de novo) identified in exon 2 has not been tested for NMD. If produced it would lead to a truncated protein with a disrupted 5th zinc-finger domain.
Genetic testing
Several of the mutations so far described were identified through whole genome sequencing (WGS), exome sequencing studies (including trio analysis), or by Sanger sequencing of the ZIC1 coding region. To date no deletions of the ZIC1 gene have been found in craniosynostosis patients, however deletion of ZIC1 and the nearby paralogue ZIC4 has been associated with isolated Dandy Walker Malformation (OMIM #220200).
Possible molecular diagnostic approaches to confirm the diagnosis in a proband include:
- Sanger sequencing of ZIC1 coding regions (single-gene testing), if the clinical suspicion of ZIC1-related craniosynostosis is high.
- Multi-gene panel screening or performing exome sequencing, if multiple differential diagnoses exist.
Clinical evaluation and targeted genetic testing of both parents for the ZIC1 variant identified in the proband is recommended, to establish if the variant was inherited or occurred de novo, to aid genetic counselling. Mosaic mutation both early post-zygotic, causing a milder phenotype, and later post-zygotic causing sibling recurrence in offspring, are possible.
